Case Studies: Turning ITAD into an Emissions-Reducing Powerhouse
Since the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, humanity has pumped greenhouse gases into the atmosphere at a rate our planet simply isn’t keeping up with. We’re now dealing with the consequences: rising global temperatures and increased human and economic risks. The good news? Businesses have more power than ever to reverse some of the damage and IT asset disposition (ITAD) is one of the most underrated tools in their arsenal.
In this article, we’ll explore how smart ITAD practices, particularly prioritizing reuse over recycling, can dramatically cut carbon emissions, reduce e-waste, and contribute to your organization’s sustainability reporting. We’ll also look at how working with the right ITAD managed service provider (MSP) can transform your IT retirement strategy into a measurable environmental win while putting money back in your budget.
Corporate Response to Environmental Challenges
Carbon dioxide may not be the most potent greenhouse gas, but it is by far the most abundant and human activity is releasing more of it than ever. From transportation to manufacturing and heating, our lifestyles and business operations are overloading the planet with emissions.
Organizations are beginning to mitigate their role in this. Whether it’s through upgrading facilities, reducing business travel, or investing in energy-efficient systems, reducing carbon is now firmly on the corporate agenda. But one of the most overlooked sources of emissions is sitting right under your nose: your IT equipment.
IT and Emissions: The Big Picture
IT devices are essential to modern operations, but their environmental impact is significant. According to the Global Electronics Council (GEC), digital technology contributes between 1.4% and 5.9% of total global greenhouse gas emissions. And here’s the kicker: over two-thirds of that comes from the manufacturing phase, not day-to-day use.
Why? Because every time a new laptop, smartphone, or desktop is built, massive amounts of raw materials are mined, processed, transported, and assembled, each step releasing emissions. For instance, the manufacture of a single laptop produces on average 243 kg of CO2e emissions. Multiply those numbers by hundreds or thousands of devices in your organization, and the footprint adds up fast.
The Hidden Impact of E-Waste
When IT assets reach the end of their life, many companies simply recycle them or—worse—send them to landfill. But this creates an entirely new set of environmental issues.
In 2022 alone, we generated 62 million metric tons of e-waste, yet only about 22% was properly recycled. The rest? Lost to landfills or informal disposal, where it leaks toxins like mercury, lead, cadmium, and flame retardants into the environment.
In the U.S., e-waste represents just 2% of total landfill content but up to 70% of landfill hazardous waste. That’s one reason why 23 states and the District of Columbia have already banned or heavily regulated e-waste landfilling—and more are on the way.
Reuse: The Real Carbon Saver
Let’s be clear: recycling is better than landfilling. But if your goal is to reduce emissions, reuse beats recycling by a landslide.
According to the EPA’s Waste Reduction Model (WARM), reusing one short ton of portable IT equipment (like laptops and tablets) prevents 29.83 metric tons of CO2e from entering the atmosphere. Recycling the same amount? Just 1.07 metric tons avoided.
That means reuse reduces nearly 28 times more emissions than recycling. It’s the ultimate form of source reduction, preventing new products from being made and the emissions that come with them.
ITAD and the Circular Economy
A circular economy isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a smarter way of doing business. Instead of taking, making, and dumping, a circular model focuses on keeping products in use for as long as possible.
In ITAD, that means:
- Refurbishing devices so they can be resold or redeployed
- Recovering components from partially working equipment
- Recycling is only a last resort
And if you're working with a quality ITAD MSP, it also means getting carbon reporting that helps you track and share your sustainability wins.
The Power of an ITAD Managed Service Provider
Not all ITAD providers are created equal. The best ones don’t just pick up your equipment; they help you maximize reuse, track avoided emissions, and recover value through resale.
Let’s break it down. A good ITAD Managed Service Provider (ITAD MSP) should offer:
- Refurbishment First – Prioritize reuse to cut emissions by up to 28 times more than recycling
- Zero Landfill Commitment – Prevent hazardous waste from harming the planet and prevent possible legal liabilities if your retired assets are discovered illegally dumped
- Data-Driven Reporting – Provide Scope 3 and Scope 4 metrics that you can directly use in your sustainability reports
- Value Recovery – Resell usable assets and generate cash that you can reinvest into your IT budget
Real-World Case Studies
Let’s take a look at two companies that partnered with ICT, a leading ITAD MSP known for its zero-landfill policy and Mission Reuse program.
Case Study: Cyber Security Firm
A cybersecurity firm engaged with ICT to handle their ITAD. This table shows the avoided emissions from reused assets.
Cyber Security Firm: Reused IT Assets
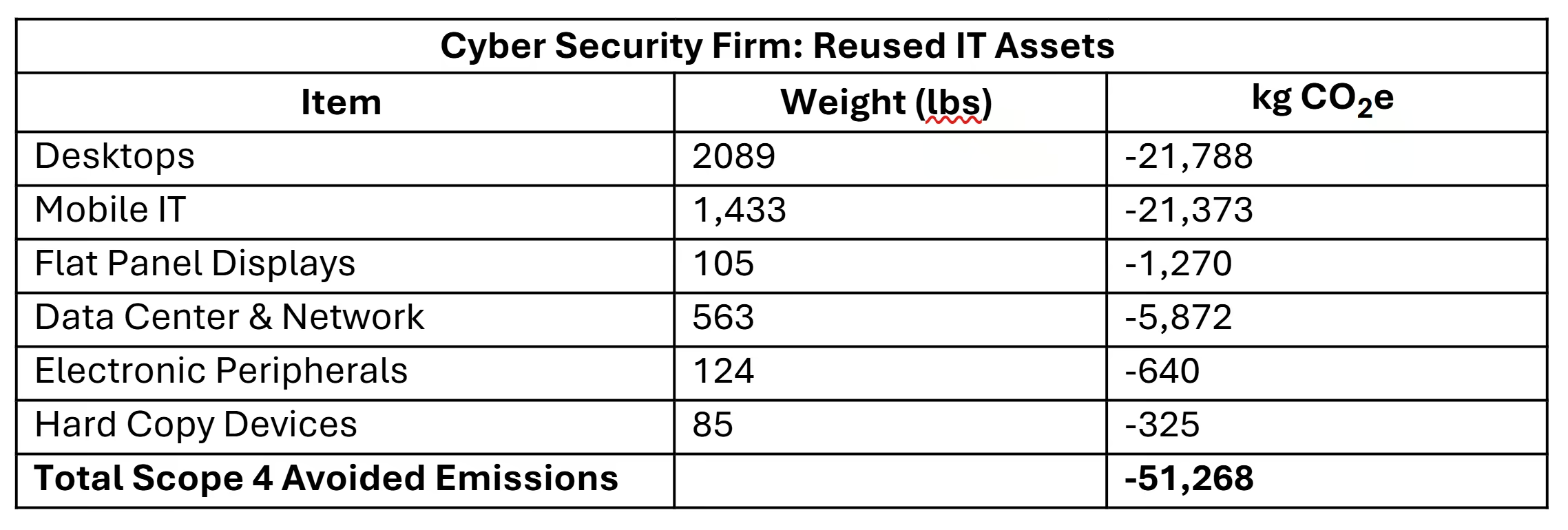
Not every device was reusable, so here are the avoided emissions from recycled assets.
Cyber Security Firm: Recycled IT Assets
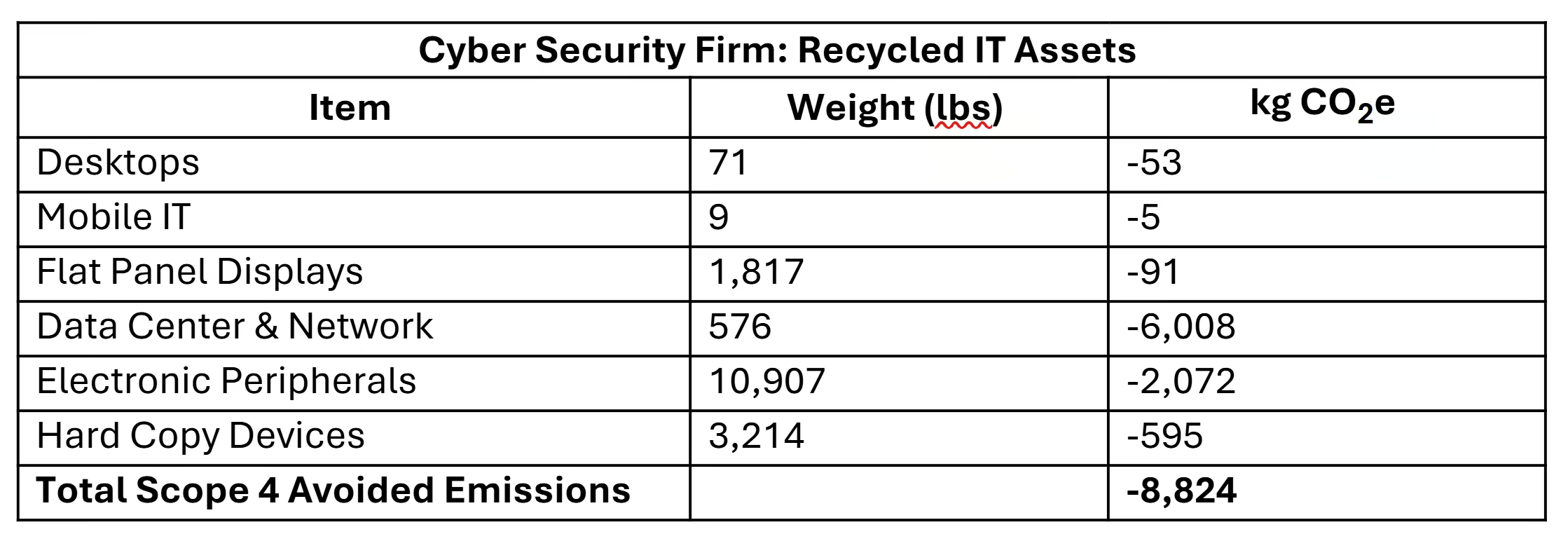
Note that by far, the majority of assets were reused rather than recycled. The total avoided emissions from reuse (-51,268) and recycling (-8,824) were -60,092 kg CO2,e which was prevented from being released into the atmosphere. That’s a successful emissions reductions project!
Case Study: Medical Services Company
Here are the avoided emissions from reused vs recycled assets from a medical services company that also worked with ICT to handle their ITAD.
Medical Company 1: Reused IT Assets
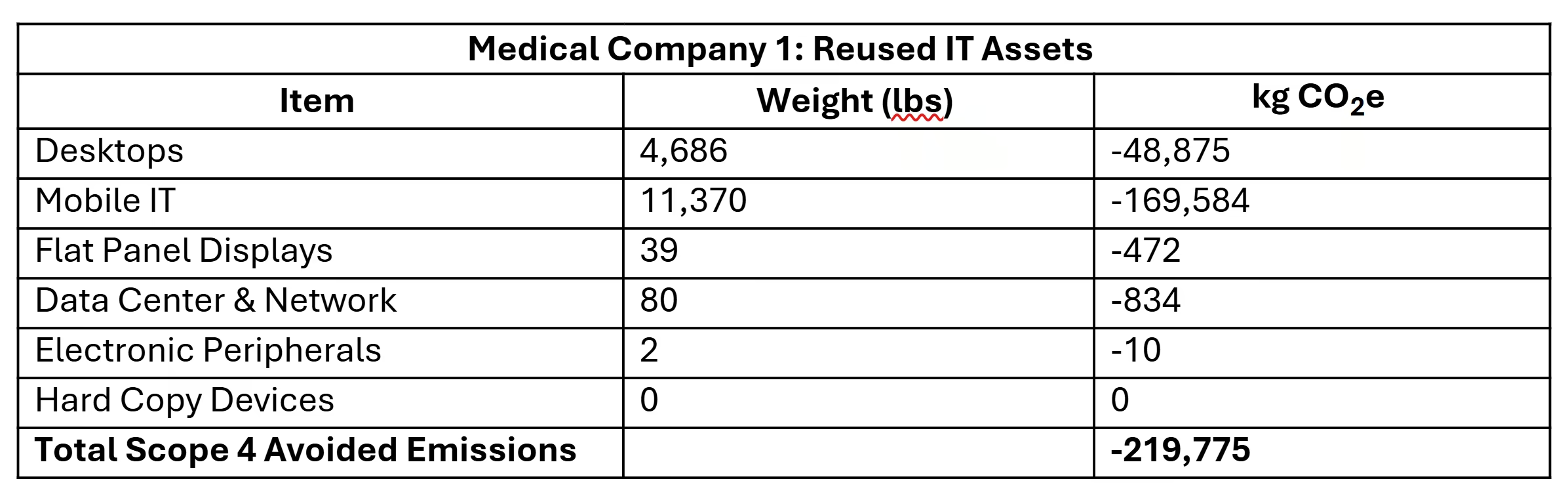
WOW! That is a lot of Scope 4 Avoided Emissions from reuse! Again, not every asset was reusable, so here are the carbon reductions from recycling.
Medical Company 1: Recycled IT Assets
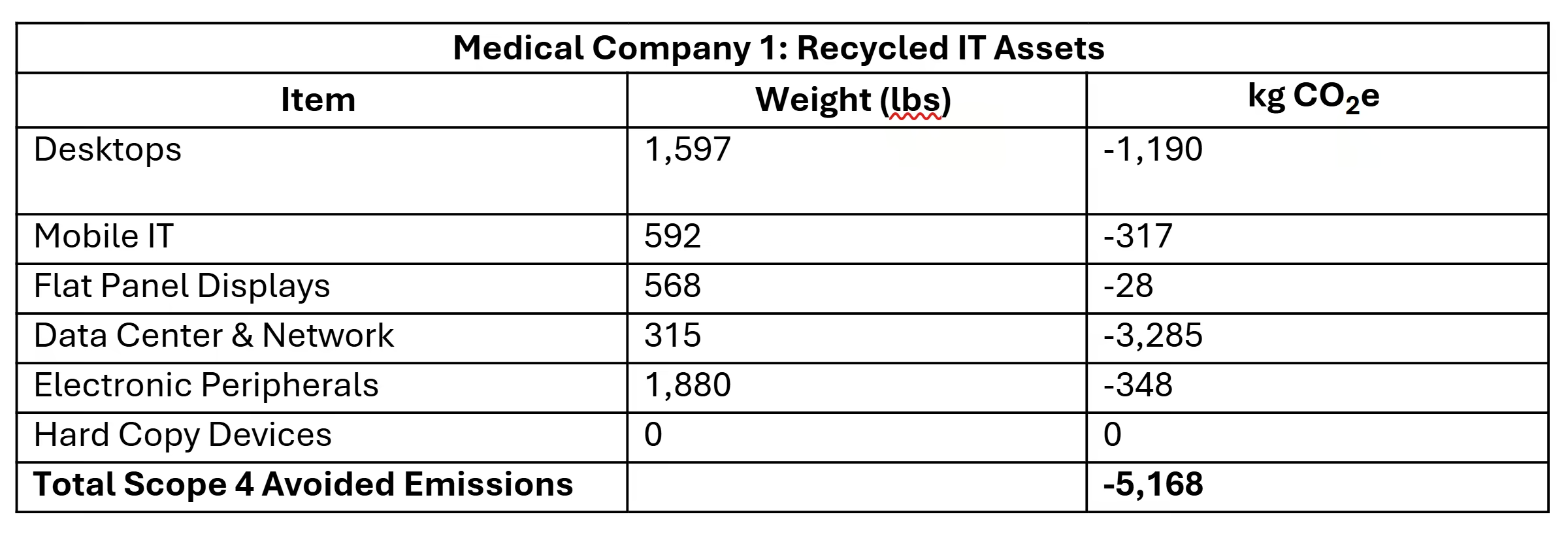
Note once again that most assets were refurbished and reused. The total avoided emissions from reuse (-219,775) and recycling (-5,168) were an amazing -224,943 kg CO2e reported as Scope 4 Avoided Emissions. That’s a huge overall emissions reduction!
The Role of Carbon Reporting: Scope 1, 2, 3, and 4
Responsible ITAD affects your Scope 3 emissions, those indirect emissions from your supply chain, but also helps you rack up Scope 4 avoided emissions, which represent the emissions prevented by others reusing your equipment.
While Scope 4 isn't yet a formal GHG Protocol category, it's increasingly being recognized in sustainability reports, particularly when clearly documented and backed by credible data.
A good ITAD provider will help you:
- Track Scope 3 transportation emissions
- Calculate emissions avoided from reuse and recycling
- Provide clear audit-ready documentation and methodology to avoid greenwashing claims
Final Thoughts: Make ITAD Part of Your Environmental Strategy
When you think of emissions reduction, you might picture solar panels, heat pumps, or electric fleets. But responsible ITAD deserves a spot on that list. It’s low-cost, high-impact, and immediately actionable.
By working with an ITAD partner like ICT that prioritizes reuse, you can:
- Cut your organization’s carbon footprint
- Meet sustainability goals faster
- Keep toxic waste out of landfills
- Unlock new value from old assets
- Report tangible, credible emissions reductions
If your company is looking to make measurable progress in environmental responsibility, it’s time to rethink ITAD not as an afterthought, but as a powerful tool. Want to see how much carbon your company could save through smarter ITAD? Reach out to ICT and ask for a personalized emissions report.
Let’s build a greener, smarter, and more circular future—one retired laptop at a time.
Selected References
ERCC (2024) Landfill Bans by State. Www.ecycleclearinghouse.org. Retrieved May 2, 2024, from https://www.ecycleclearinghouse.org/contentpage.aspx?pageid=101
GEC, (2021). State of sustainability research: Climate change mitigation. Global Electronics Council https://globalelectronicscouncil.org/wp-content/uploads/GEC_Climate_Change_SOSR_DRAFT_For_Public_Comment_1APR2021.pdf
ICT Mission Reuse (n.d.) ICT Mission Reuse. Retrieved April 8, 2024, https://mission-reuse.com/
Singh, N., & Ogunseitan, O. A. (2022). Disentangling the worldwide web of e-waste and climate change co-benefits. Circular Economy, 1(2), 100011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cec.2022.100011
UNITAR. (2024, March 20). Global e-Waste Monitor 2024: Electronic Waste Rising Five Times Faster than Documented E-waste Recycling. United Nations Institute for Training and Research. https://unitar.org/about/news-stories/press/global-e-waste-monitor-2024-electronic-waste-rising-five-times-faster-documented-e-waste-recycling
US EPA WARM (2019) Documentation for Greenhouse Gas Emission and Energy Factors Used in the Waste Reduction Model (WARM) Electronics. US Environmental Protection Agency. https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2019-06/documents/warm_v15_electronics.pdf
©ICT Inc. 2024-2034. All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of this article, in whole or in part, without proper attribution to ICT Inc. is strictly prohibited.
