Donating IT assets can bring immense benefits to your organization, the environment, and society. However, there are key considerations to make the most of your donation, avoid unnecessary risks, and comply with regulations.
Benefits of Donating IT Assets
- Community Goodwill: Donating IT equipment helps bridge the digital divide, providing technology access to those who might otherwise go without.
- Environmental Impact: By giving technology a second life, donations reduce electronic waste and keep materials out of landfills.
- Tax Benefits: Donations can offer clear tax advantages when handled correctly.
- Brand Enhancement: Donating thoughtfully can improve corporate social responsibility scores, align with sustainability goals, and strengthen brand reputation.
Dangers of Donating IT Assets Directly
- Data Security Risks: Direct donations without proper data destruction can expose sensitive information, potentially leading to costly data breaches. Without following strict protocols (such as NIST 800-88), donors could face legal consequences and hefty fines.
- Compliance Risks: If the charity does not want the assets and disposes of them, environmental laws, such as the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA), enforce strict handling and disposal of e-waste and hold companies responsible for cradle-to-grave liability. Violations could lead to costly cleanups and brand damage.
- Operational Burden on Charities: Nonprofits often lack the resources to process, refurbish, or dispose of incompatible or obsolete equipment, which can turn donations into a financial burden rather than a benefit.
- Potential Brand Damage: Unwanted assets that end up in landfills or illegitimate recycling channels could harm the donor's reputation, as could donating used assets to a charity that sees them as a burden rather than a benefit.
- Tax Risks: When asset donations are not handled correctly, and the proper appraisals and forms are not filled out, the IRS could disallow the donation. Even if a Donor Advised Fund (DAF) is utilized and handles the appraisals, there are additional costs and risks of those assets not being used by a charity. Furthermore, the IRS recognizes that some DAFs have been set up for the purpose of generating questionable charitable deductions; if your DAF is investigated, you may get audited as well.
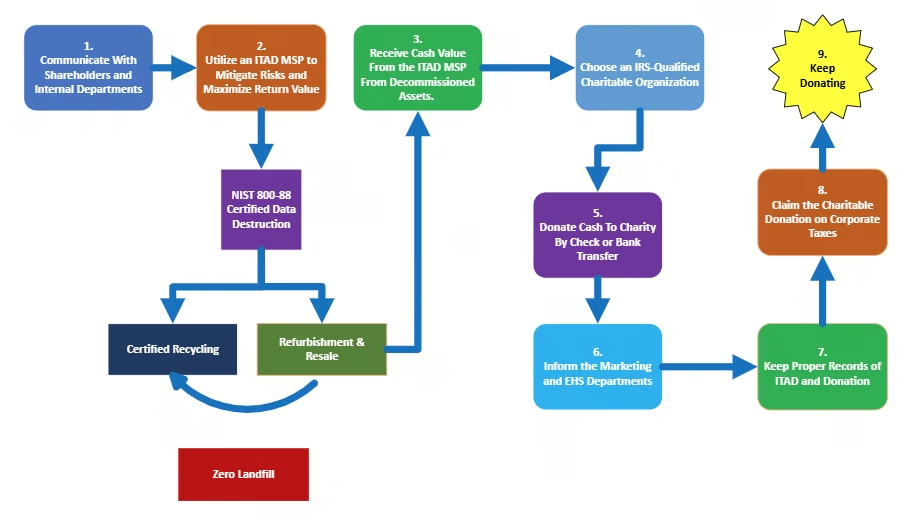
9 Steps to Successful IT Asset Donations
Here’s a step-by-step guide to streamline the process and achieve a successful, impactful IT donation.
1. Engage Stakeholders and Departments Early
- Why: Approval from shareholders is essential for charitable donations, as uncoordinated contributions can impact shareholder value and may even be viewed as a breach of fiduciary duty. Donating IT assets directly involves not only potential risks if mishandled but also processing costs, ranging from $15 to $50 per asset or up to $100 or more when repairs and software installations are required, drawing directly from shareholder resources. Additionally, shareholders may prefer to retain the residual asset value within the company, or they may wish to support charitable initiatives in a way that aligns with both corporate objectives and financial responsibilities. Clear communication ensures that charitable actions are both financially sound and shareholder-supported.
- How: Brief shareholders, IT, marketing, cyber security, and corporate social responsibility departments about the plan to ensure brand-building, risk management, and compliance with stakeholder goals and social responsibility objectives.
2. Partner with an IT Asset Disposition Managed Service Provider (ITAD MSP)
- Why: Direct donations carry cybersecurity and compliance risks, along with refurbishment costs. An ITAD MSP ensures data security, environmental compliance, and brand protection while providing 3rd-party certification of compliant disposal and data destruction. These certifications are more audit-proof than self-certification, offering stronger immunity in case of issues. Partnering with an ITAD MSP also relieves your internal teams from managing refurbishment, testing, and repairs, ensuring full compliance, risk mitigation, and operational efficiency.
- How: Engage ITAD MSPs to professionally handle all aspects of IT asset disposition—from secure data destruction to refurbishment, remarketing, and responsible recycling of non-reusable equipment.
3. Receive the Cash Value from Refurbished IT Assets
- Why: Receiving cash from an ITAD MSP simplifies the process by eliminating the need for asset valuation, IRS form filings, or independent appraisals required for tax-deductible donations. ITAD MSPs manage resale and recycling, maximizing the cash value returned to you while also providing certificates of compliant recycling and data destruction for your records, ensuring full compliance and audit readiness.
- How: After processing the equipment, the MSP will issue payment, reports, and certifications, offering a straightforward path with a clear paper trail for donating the cash value to your chosen charity.
4. Select a Qualified Charity
- Why: To qualify for tax benefits, the receiving organization must be registered as a charitable organization with the IRS.
- How: Verify the charity’s status via the IRS or request confirmation from your chosen organization.
5. Donate the Residual Cash Value
- Why: Cash donations are easier to document, appraiser-free, and pose no risk of non-compliance or asset obsolescence for the charity. Furthermore, by donating cash, the charity can allocate funds based on its most pressing needs, which may or may not be technology.
- How: Simply write a check for the received cash amount, creating a clear paper trail and reducing all tax-related ambiguities.
6. Inform Marketing, PR, Accounting and EHS Departments
- Why: Publicizing the donation amplifies corporate social responsibility and brand value. It also enables departments to track and report sustainability achievements.
- How: Provide certificates of disposal, data destruction, and any avoided carbon dioxide emissions reporting from the ITAD MSP to relevant departments for records and reporting.
7. Maintain Thorough Documentation
- Why: Detailed records ensure IRS compliance and streamline potential future internal and external audits.
- How: Retain donation receipts, tax documentation, and all ITAD process records, such as certificates of data destruction and responsible recycling. Proper documentation from the ITAD MSP makes it easier to meet both IRS and regulatory standards.
8. Claim the Cash Donation on Corporate Taxes
- Why: Cash donations qualify for tax deductions without the need for third-party appraisals, simplifying the filing process.
- How: File Schedule A (Form 1040) and maintain records of your cash donation to claim the deduction on your next corporate tax return.
9. Repeat the Process Regularly
- Why: Donations of cash received from refurbished IT create a cycle of goodwill, brand enhancement, and positive social impact while furthering a circular economy when assets are destined for reuse outside your organization. Furthermore, charities will always appreciate cash donations that they can use for their most pressing needs, rather than aging IT assets, which may not fit their needs.
- How: Make this process a regular part of your IT upgrades and inform your ITAD MSP of your plans. In your next ITAD cycle, you can donate to the same organization or choose a new one every time to spread the benefits around.
By following these steps, your organization can maximize the benefits of IT donations, protect its brand, mitigate ITAD-related risks, and streamline the path to tax compliance while making a meaningful impact on the community.
Find Out How We Can Help
For more information on this important topic, check out our white paper on donating IT assets. Or, if you are an enterprise, government, or institution looking for ITAD services or you have additional questions, please contact ICT today!
Selected References
Bloomberg Law. (2023, December 12). Consumer Data Privacy Laws. https://pro.bloomberglaw.com/insights/privacy/consumer-data-privacy-laws/#how-privacy-laws-work
ICT Mission Reuse (n.d.) ICT Mission Reuse. https://mission-reuse.com/
IRS. (n.d.) Charitable Organizations - Substantiating Noncash Contributions | Internal Revenue Service. Www.irs.gov. https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/charitable-organizations/charitable-organizations-substantiating-noncash-contributions
IRS DAF. (n.d.) Donor-Advised Funds | Internal Revenue Service. Www.irs.gov. https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/charitable-organizations/donor-advised-funds
IRS Tax Exempt Organizations. (2019) Tax Exempt Organization Search | Internal Revenue Service. Irs.gov. https://www.irs.gov/charities-non-profits/tax-exempt-organization-search
Kissel, R., Regenscheid, A., Scholl, M., & Stine, K. (2014, December 17). Guidelines for Media Sanitization. Csrc.nist.gov. https://csrc.nist.gov/pubs/sp/800/88/r1/final
US EPA. (2018, August 15). Summary of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act | US EPA. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-resource-conservation-and-recovery-act
©ICT Inc. 2024-2027. All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of this article, in whole or in part, without proper attribution to ICT Inc. is strictly prohibited.
