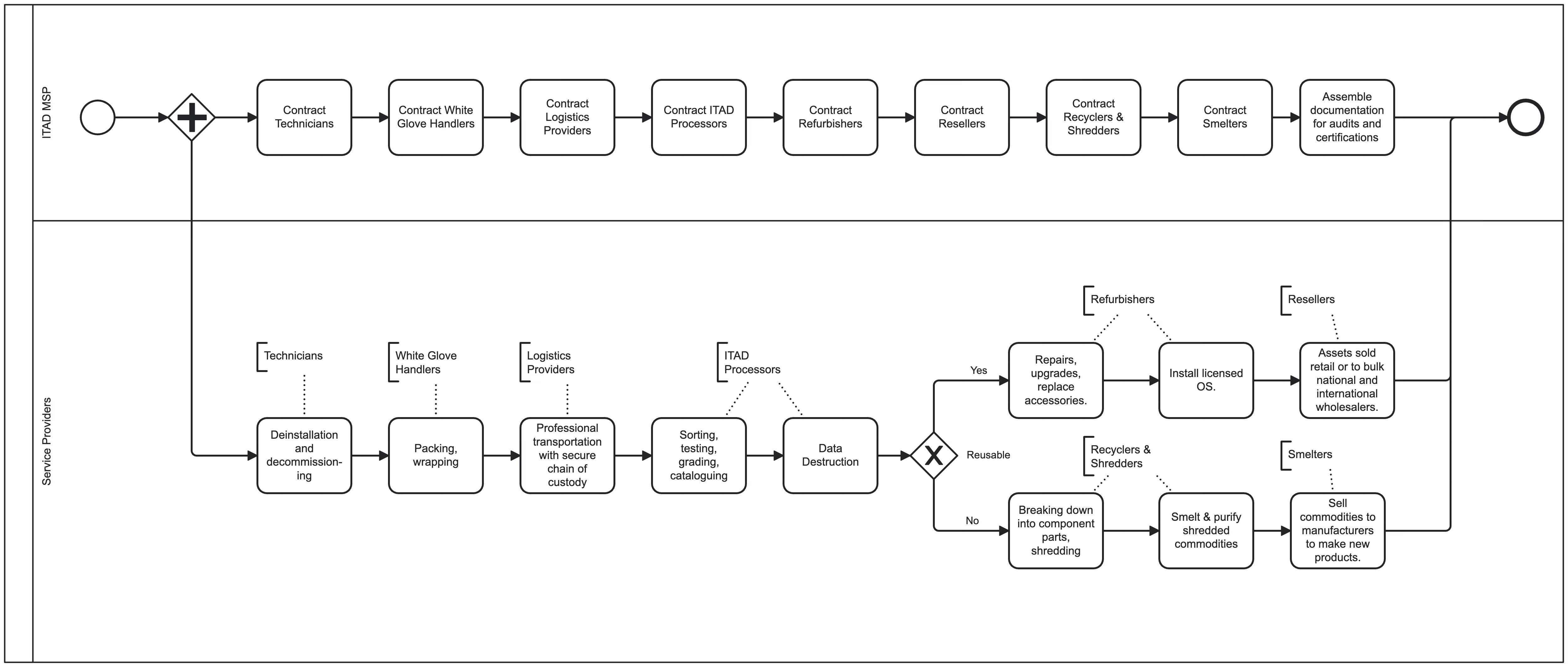
In the complex world of IT Asset Disposition (ITAD), various types of companies play distinct roles, each with their own capabilities, limitations, and associated risks. Here’s an overview of each group involved in ITAD—their strengths and where they may fall short. Finally, we’ll explore how an ITAD Managed Service Provider (ITAD MSP) minimizes risks and maximizes value by integrating these roles into a streamlined, compliant solution. Let’s dive in!
1. Logistics Companies
- What They Do: Logistics companies primarily handle the physical transport of IT assets. They may or may not offer services such as packing, palletizing, labeling, and on-site scanning for asset tracking. These services help streamline the delivery process, reducing the burden on clients to manage the physical aspects of asset relocation.
- What They Don’t Do: Logistics companies typically lack ITAD-specific expertise, such as secure packaging to protect IT assets in transit, secure chain-of-custody protocols, data destruction, and refurbishment. Without specialized IT handling knowledge, logistics teams risk damaging assets, reducing their value, or worse, causing data security breaches or environmental issues that could lead to fines and litigation.
2. ITAD Processors
- What They Do: IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) processors are responsible for managing retired IT assets, including tasks such as testing, grading, data destruction, and cataloging for reporting and certification. However, they typically do not handle hazardous materials directly. Instead, they identify components containing hazardous substances—such as batteries, mercury-containing devices, and certain circuit boards—and ensure these are directed to specialized facilities equipped to manage hazardous waste in compliance with environmental regulations. This approach aligns with the Responsible Recycling (R2) Standard, which emphasizes the proper handling and disposal of hazardous materials to minimize environmental impact.
- What They Don’t Do: While ITAD processors excel in data security and regulatory compliance, they typically don’t offer logistics services or local pickup, typically within a 100-mile radius of the facility. This means companies need separate providers for transport, especially if the project involves multiple locations across the country. Additionally, ITAD processors may specialize in certain types of assets (e.g., Windows devices, networking equipment, iOS-based equipment, mobile phones, etc.), so their effectiveness varies significantly across asset classes and may result in reusable assets being sent to recyclers simply because they lack the expertise to handle them. They also typically do not manage the refurbishing of assets for resale or the actual recycling process; instead, these tasks are assigned to a select group of specialized third-party handlers.
3. Commodity Recyclers (Shredders)
- What They Do: Recyclers break down non-reusable IT assets into commodities, separating materials like metals, plastics, and glass for remanufacturing. They then shred those materials and sell them to smelters, who turn them into new raw materials that can be sold to manufacturers to make new products
- What They Don’t Do: Recyclers focus on resource recovery, not reuse, and typically do not assess items for refurbishment, often resulting in the unnecessary destruction of reusable assets. While they can provide bulk certificates of disposal, they usually lack the capability to deliver detailed reports and chain-of-custody documentation for each asset, leaving clients without the comprehensive records needed for verification and audits.
4. Waste Management Organizations
- What They Do: General waste management companies are skilled at handling large-scale waste removal and are often engaged in takedowns of old office furniture, equipment, and other non-specialized waste. They efficiently manage logistics and the disposal of general waste.
- What They Don’t Do: General waste management companies are not ITAD specialists and lack secure data destruction capabilities, posing data security and compliance risks. While they may sell obviously reusable items, they typically do not sort, refurbish, or test IT equipment, often leading to unsafe disposal or improper resale. They also lack expertise in e-waste regulations and responsible recycling and cannot certify compliant electronic disposal and data destruction, increasing environmental and legal risks for clients.
5. Used Equipment Dealers
- What They Do: Used equipment dealers buy and sell IT assets, trying to sell them for the best price they can get and offering clients a quick cash return on unwanted equipment. They serve as a quick way to offload assets without going through extensive ITAD processing.
- What They Don’t Do: Used equipment dealers often bypass essential ITAD steps, such as testing, data eradication, refurbishing, removing the original owner’s identifiers from equipment, OS installation, and thorough documentation of disposal. Additionally, dealers typically lack the expertise and certification authority to provide data destruction reports, issue necessary certificates, or responsibly manage non-reusable assets through certified downstream partners. Mishandling of the OS can result in unauthorized or illegal use by third parties, further increasing cybersecurity, environmental, and legal risks, and exposing the original owner to potential financial and reputational harm.
ITAD Managed Service Providers (MSPs): Industry Integrators
While each of the above groups plays a critical role in ITAD, gaps in their services mean companies would need to coordinate multiple providers for a complete, secure, and compliant ITAD process. Effective ITAD requires attention to data security, environmental responsibility, and maximizing the value of each asset, which only a well-coordinated approach can achieve.
ITAD Managed Service Providers (MSPs) are specialized industry integrators that bring together every aspect of IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) under one umbrella, filling in those missing gaps and closing the loop with maximum efficiency without cutting corners. By managing the entire lifecycle of retired IT assets, ITAD MSPs ensure the various stages of disposition work cohesively, minimizing risk, maximizing residual asset value, and simplifying the process for their clients while producing audit-ready records at the end of it all. Here is what an ITAD MSP does for you.
1. Comprehensive ITAD Planning and Logistics Coordination
The ITAD MSP begins by obtaining a complete list of assets to be retired and creating a customized plan. They use a vetted network of logistics providers and IT relocation specialists to ensure the assets are handled properly, based on the specific needs of each location. For instance, they may arrange white-glove technology removal services for office equipment, where assets are meticulously packed and skidded, ready for safe transportation. In contrast, technicians may be dispatched for data center decommissioning projects, where a higher level of technical skill is required, followed by technology relocators to package and get it ready for shipping. This tailored approach reduces the risk of damage, loss, and data breaches associated with improper handling.
MSPs also coordinate logistics by partnering with reputable trucking companies that specialize in high-value cargo. These logistics providers follow a secure loss prevention protocol, maintaining a strong chain of custody documentation. Precautions may include, if necessary, using, in some cases, tamper-evident seals or direct delivery for especially sensitive materials, protecting against risks of loss or data exposure during transit.
2. Selecting Certified Processors for Secure Data Destruction and Asset Recovery
Once the IT assets arrive at their destination, ITAD MSPs send them to R2 or e-stewards certified processors who excel in secure data destruction, asset categorization, and responsible recycling. The ITAD MSP knows which processor to use for which range of assets since no single processor can be an expert in everything.
These processors follow strict data destruction protocols, such as NIST 800-88 or equivalent, to eliminate any residual data, minimizing the risk of data breaches. Assets are carefully sorted, graded, and tested to determine which items can be reused and which should be recycled. This streamlined categorization not only maximizes value recovery but also supports the circular economy by prioritizing reuse over recycling. When assets are non-reusable, they know how to sort them so that hazardous components are sent to special hazardous waste handlers, while others can be sent to commodity recyclers for shredding and smelting.
3. Specialized Refurbishment and Resale
ITAD MSPs have relationships with a wide range of refurbishers who specialize in specific types of equipment and, again, know who to send which equipment to. This may include specialists in mobile devices, Windows or Apple-based equipment, medical technology, or POS systems, just to name a few. Refurbishers repair these specialized assets, replace any missing accessories, and install licensed operating systems, making them ready for resale. By choosing refurbishers who are experts in each asset type, MSPs can optimize resale value, extend the life of each product, and make high-quality devices available to secondary markets at affordable prices.
4. Environmentally Responsible Recycling for Non-Reusable Items
For items that are deemed non-reusable, ITAD MSPs partner with commodity recyclers. These professionals sort and shred non-reusable equipment in a professional and responsible manner, ensuring they do not end up in landfills or are exported in violation of the Basel Convention, which regulates international transport of hazardous materials. ITAD MSPs follow best practices, often implementing a zero-waste policy to ensure that no e-waste ends up in landfills, aligning with state regulations that have banned e-waste disposal in many regions.
5. Centralized Documentation and Tracking for Full Transparency
One of the more significant advantages of using an ITAD MSP is the centralization of documentation across all ITAD stages. By consolidating each processor and handler's certificates and records, including recycling and data destruction certificates, the MSP creates a comprehensive, audit-proof report. They compare asset weights received by the logistics company, tracing every item by serial number through each processor and refurbisher to its final disposition, whether recycling or resale, to ensure no asset is lost, misplaced, or unaccounted for. ITAD MSP also consolidates and manages the logistics records to support a solid chain of custody.
For companies with multiple locations, ITAD MSPs streamline what could otherwise be a logistical nightmare. Instead of separate documentation for each site, MSPs provide unified reporting that is easy to interpret and compatible across locations. They also offer online portals that enable clients to track assets in real time, download certificates on demand, and receive customizable audit-ready reports. This level of transparency helps companies maintain compliance, meet regulatory standards, and protect themselves in case of disputes or audits.
6. Cost Efficiency and Maximizing Asset Value
ITAD MSPs do not just offer convenience—they provide significant cost savings. By optimizing each step of the ITAD process and maintaining partnerships with logistics providers, processors, and refurbishers, they reduce handling costs, minimize risks, and maximize asset recovery value. This level of integration allows companies to potentially offset their ITAD costs, and many can even generate revenue from their retired assets, which can be reinvested in their IT budgets or donated to charity.
7. ITAD Advice
Finally, ITAD MSPs should freely offer ITAD advice to their clients and the general public about how to create a more secure, financially beneficial, and environmentally responsible ITAD process.
With the help of ITAD MSPs, companies can focus on their core business functions, ensuring that every step of the IT asset disposition process is handled efficiently, securely, and responsibly.
Find Out How We Can Help
If you are an enterprise, government, or institution looking for ITAD solutions or you have additional questions, please contact us at ICT. You can also look at our Industry Integrator white paper for more in-depth information on this topic.
Selected References
Basel Convention. (2011). Www.basel.int. https://www.basel.int/TheConvention/Overview/tabid/1271/Default.aspx
ERCC. (n.d). Map of States With [E-waste] Legislation. Www.ecycleclearinghouse.org. https://www.ecycleclearinghouse.org/contentpage.aspx?pageid=10#:~:text=There are currently 25 states
Kissel, R., Regenscheid, A., Scholl, M., & Stine, K. (2014). Guidelines for Media Sanitization. Guidelines for Media Sanitization, 1. https://doi.org/10.6028/nist.sp.800-88r1
SERI - Sustainable Electronics Recycling International. (2013). Sustainableelectronics.org. https://sustainableelectronics.org/
US EPA, O. (2016, February 1). Certified Electronics Recyclers. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/smm-electronics/certified-electronics-recyclers
©ICT Inc. 2024-2027. All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of this article, in whole or in part, without proper attribution to ICT Inc. is strictly prohibited.
