Handling IT asset disposition (ITAD) might seem daunting, with risks of data breaches and environmental contamination. Those risks are multiplied with large companies with diverse assets across multiple locations, creating a complex ITAD process that must be handled correctly. Regardless of the size of your company, these risks, as well as other factors, can make ITAD an unnecessary financial burden. Fortunately, however, with the right approach, you can mitigate the risks, keep your company safe, and recover residual asset value to put back into your IT budget. Let’s learn how!
When Should IT Assets Be Replaced?
In an ideal world, reducing the frequency of ITAD would be the best way to mitigate the risks associated with that. However, we don’t live in an ideal world. Our tech is rapidly becoming outdated, with some manufacturers using planned obsolescence to promote more frequent upgrades than should be necessary. Therefore, replacing IT isn’t really an option for most of us; it’s a necessity.
Financial Risks of Keeping Old Tech
When you keep old tech for too long, maintenance costs can spike, doubling after four years, while the risk of breakdowns also increases 2-3 times. Old tech can also significantly reduce employee productivity, increase employee turnover, and increase the risks of costly downtime, which for most enterprise-level companies costs anywhere from about $1600 to millions of dollars for every single minute of downtime.
Strategic Tech Replacement
While replacing tech has environmental consequences, keeping old tech poses serious financial risks for your company. When your management team tracks the costs of maintaining your assets and chooses the right time to replace them before they lose too much value, it can encourage their reuse in secondary markets. This can recover significant value that you can put back into your IT budget, all while ensuring a circular economy with positive environmental and social outcomes. This is because it prevents e-waste from entering landfills or recycling streams and puts tech in the hands of those who otherwise might not be able to afford it.
Avoiding Data Breaches
When retired assets are not handled correctly, are illegally disposed of, or a meticulous chain of custody is not followed, it could lead to costly data breaches, which could result in possible fines and lawsuits and serious damage to your brand reputation. Here is how you can minimize these costly risks.
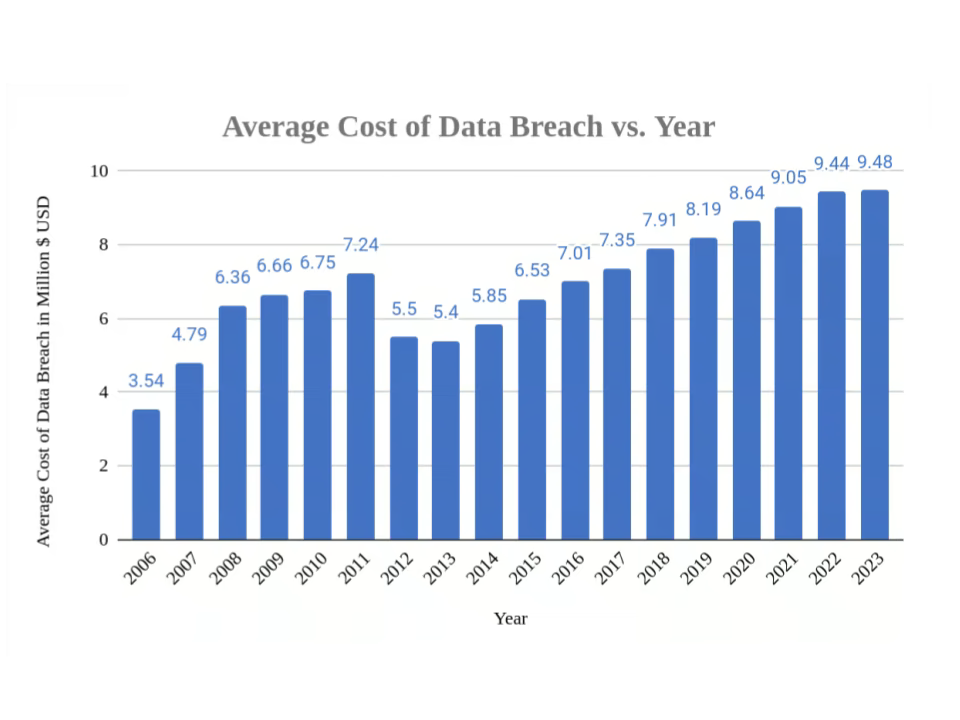
Image: The Cost of Data Breaches in the USA, Data from Statista.
In-House Data Wiping
Before handing assets to an ITAD provider, do your own in-house data wiping to improve reusability and protect against breaches. Middle management should train IT users to wipe data and remove locks and passwords. While this is not secure data wiping, it still adds that extra layer of protection and helps ensure the asset can be reused.
Adherence to Strict Data Destruction Standards
Your chosen provider should adhere to stringent NIST 800-88 r1 data destruction procedures, including verification of destruction. They should offer an online portal so you can access your certificates of data destruction and verify for yourself that your assets have been handled properly and professionally.
Be wary of companies that are not transparent about what standards they use or try to pass the responsibility on to others. You want a provider who makes your company’s data security a top priority.
Environmental Contamination
Increasingly across the USA, states are strictly regulating or banning landfilling of e-waste due to the environmental and health hazards they present when heavy metals, flame retardants, and other toxic compounds are released into our soils, air, or water. If your waste is discovered causing environmental contamination, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act holds companies liable for all clean-up and litigation costs.
Ideally, choose an ITAD provider with a zero-landfill policy so that you know your retired assets will never end up in landfills, so that you don’t have to worry about potential fines, litigation, or damage to your brand reputation if they are discovered there.
Promoting Reuse
Another way to ensure your retired assets do not cause environmental contamination is by promoting reuse. Educate your staff to keep assets maintained in top condition so that they can be refurbished and resold, ensuring environmental responsibility.
Use Only Vetted Certified E-Waste Recycler
For assets that can no longer be reused, your provider must use only vetted and e-stewards or R2 certified e-waste recyclers located in the USA. This ensures a closed-loop process that will avoid the dangers of illegal disposal or overseas shipment to informal recycling centers in violation of the Basel Convention. Do your due diligence by verifying certifications and requesting appropriate documentation on compliant recycling.
Maintain Comprehensive Documentation
Every step of the ITAD process should be documented meticulously. This includes asset types, serial numbers, conditions, and final destination. Your ITAD provider should offer audit-proof documentation through an online portal to simplify this process.
You will also need all of your data destruction certificates so you can verify that all drives were sanitized or physically destroyed. Certificates of responsible recycling should also be made available and documented. Additionally, performing in-house audits can help you stay up to date with the industry's best standards.
Align ITAD with Corporate Policies
Align your corporate sustainability goals with your technology lifecycle policies. This involves all levels of corporate governance and results in a stronger, socially responsible position when all levels of employees know their responsibilities regarding IT assets and why those procedures are in place. This also enhances productivity, employee retention, and brand reputation.
Case Study: ICT, an ITAD managed service provider, provided a comprehensive ITAD solution for a leading risk management software provider, collecting 2,620 lbs. (3 skids) of IT equipment from their Chicago location. They issued a Certificate of Disposal and Data Destruction for 406 assets and 230 HDDs. Their responsible recycling and zero-waste policies ensured that no environmental contamination occurred.
Final Thoughts
Choosing the right time to retire your assets while they can still be reused, training employees in the importance of maintaining assets to encourage reuse, performing in-house wiping, using ITAD providers who use stringent data destruction services and certified e-waste processors, and maintaining comprehensive documentation will all help you mitigate risks associated with ITAD. By following these steps, you can navigate the complexities of ITAD with confidence and ensure that your company remains secure, sustainable, and ahead of the curve.
Find Out How We Can Help
If you are an enterprise, government, or institution looking for ITAD solutions or you have additional questions, please contact us at ICT. You can also check out our white paper, ITAD in Today’s Circular Economy, exploring this concept in depth.
Selected References
Basel Convention. (2011). Www.basel.int. https://www.basel.int/TheConvention/Overview/tabid/1271/Default.aspx
Bloomberg Law. (2023). Consumer Data Privacy Laws. https://pro.bloomberglaw.com/insights/privacy/consumer-data-privacy-laws
Compucom (2023). Data and analysis from our in-depth survey of hybrid worker IT experiences -and insights for improving them Connecting the Dots: Experience, Technology, and the Hybrid Work Environment Research Findings. Compucom White Paper. https://www.compucom.com/
DiDio, L. (2020). Forty Percent of Enterprises Say Hourly Downtime Costs Top $1Million – Information Technology Intelligence Consulting. https://itic-corp.com/forty-percent-of-enterprises-say-hourly-downtime-costs-top-1million/
ERCC. (n.d). Map of States With [E-waste] Legislation. Www.ecycleclearinghouse.org. https://www.ecycleclearinghouse.org/contentpage.aspx?pageid=10#:~:text=There are currently 25 states
Kissel, R., Regenscheid, A., Scholl, M., & Stine, K. (2014). Guidelines for Media Sanitization. Csrc.nist.gov. https://csrc.nist.gov/pubs/sp/800/88/r1/final
Martini, D. (2023). Wasted Talent: Time Lost to (Old) Tech Issues. Electric. https://www.electric.ai/blog/wasted-talent-time-lost-to-tech-issues
Microsoft News. (2018). True cost of not replacing computers revealed in Microsoft study: more than $4,000 each – New Zealand News Centre. News.microsoft.com. https://news.microsoft.com/en-nz/2018/10/16/true-cost-of-not-replacing-computers-revealed-in-microsoft-study-more-than-4000-each/#_ftnref1
US EPA. (2018, August 15). Summary of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act | US EPA. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-resource-conservation-and-recovery-act
SERI - Sustainable Electronics Recycling International. (2013). Sustainableelectronics.org. https://sustainableelectronics.org/
Statista. (2024). Cost of a data breach in the U.S. 2024 | Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/273575/us-average-cost-incurred-by-a-data-breach/#:~:text=Published by Ani Petrosyan%2C Sep
Unisys (2023). From Surviving to Thriving in Hybrid Work Comprehensive data and insights Hybrid work IT support Security Technology Employee experience Motivation and engagement. https://www.unisys.com/siteassets/microsites/hfs-insights/hfs-comprehensive-data-and-insights-report.pdf
©ICT Inc. 2024-2027. All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of this article, in whole or in part, without proper attribution to ICT Inc. is strictly prohibited.
