The Hidden Dangers of DIY IT Asset Disposition

When it comes to IT asset disposition (ITAD), it’s not just about getting rid of old equipment. It involves understanding data security, compliance with industry regulations, environmental responsibility, and good corporate governance. We work closely with our clients, asking for feedback and what issues they have had with ITAD in the past. Using that feedback, and our own internal research we conducted, we bring you an analysis of the hidden dangers of DIY IT asset disposition. Companies sometimes view DIY ITAD as a cost-saving measure, but this can lead to severe financial consequences if mistakes are made due to a lack of understanding or not staying current with industry best practices. The internal resources it takes to handle DIY can often exceed the cost of hiring professionals. Furthermore, DIY processes are also unlikely to maximize residual asset value, resulting in further financial losses.
The Complex ITAD Process
Managing IT asset disposition is a complex, multi-step process that includes white glove removal, transportation and logistics, equipment audit, testing, data sanitization, refurbishing, repurposing, and recycling. ITAD complexity is multiplied for large businesses because they have a large volume of equipment across multiple asset classes from multiple manufacturers with multiple lifecycles and ownership types (lease vs ownership). Those assets are also distributed across multiple locations across the states and sometimes across different countries. This creates an ITAD process that is far more complex and riskier than it already is for smaller companies with fewer assets.
Transparency in the chain of custody, adequate certifications from processors, recyclers, and data destruction services, as well as comprehensive audit-proof documentation, are crucial to avoid potential pitfalls. If you plan to DIY, you must be well educated in all these aspects to ensure a safe, efficient, and financially beneficial process. Here are some of the concerns you must be aware of.
Internal Cost of DIY ITAD
People considering DIY ITAD often underestimate just how much the entire process will cost them. Employing internal resources for auditing, testing, wiping, cataloging, refurbishing, or otherwise preparing equipment for reuse and recycling, as well as packing, palletizing, or any other DIY activity, costs much more in labor and material than using outside professional organizations specializing in technology disposal whose process is streamlined and optimized for those tasks. This means that even if it is done correctly, it still does not save any money since so much labor and other resources will go into the process. This is why many DIYers end up cutting corners, exposing themselves to risks. Those risks, if realized, will cost far more than the labor and resources that went into it; it can cost you your brand reputation and erode customer trust.
Liability Misconceptions
A common misconception is that sending IT equipment to a recycler, used equipment broker, e-waste, or general waste management company absolves the company of any further responsibility. However, various industry regulations and legal frameworks hold companies liable if their old equipment is improperly disposed of and causes a data breach or environmental damage. This is why a thorough, up-to-date understanding of the entire process and its implications is critical to protect companies' brand reputation and bottom line.
Data Breach Risks
A significant concern with DIY asset disposition is the potential for data breaches. The financial costs of data breaches far outweigh any perceived savings from DIY approaches. The average cost of a data breach in the U.S. was a whopping $9.48 million in 2023, with some costing far more than that. There are hundreds of federal and state laws that govern data security and privacy. A data breach could lead to severe financial and legal repercussions, not to mention damage to your brand reputation if your customers’ information ends up in the wrong hands.
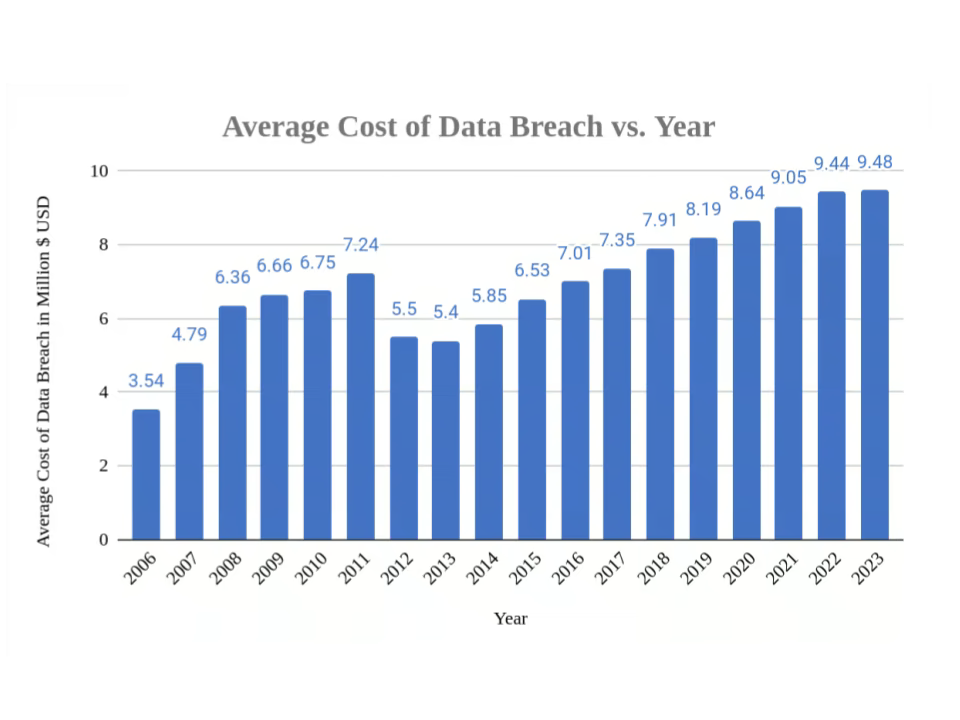
Image: Average Cost of Data Breach in the USA. Data from Statista (2024).
Inadequate Documentation and Audits
Thorough documentation of the entire disposition process is crucial for compliance with industry regulations. A reputable ITAD managed service provider (ITAD MSP) ensures proper documentation and certifications, recording serial numbers and asset descriptions. They will also reconcile that information at the end of the process to ensure complete asset traceability during internal or external audits.
DIY measures often lack the necessary expertise to ensure comprehensive documentation and reconciliation, exposing companies to risks, including fines and serious reputational damage. Without third-party certification, if your disposal process is self-certified, you will remain solely accountable for any failures.
Risks of E-Waste
If companies do not understand the certifications and processes required to recycle e-waste ethically, they risk serious trouble. Even if they understand the certifications but do not thoroughly vet their downstream vendors or their process lacks an appropriate chain of custody, their e-waste could still end up in landfills or illegally shipped overseas instead of being compliantly recycled or responsibly reused. Cradle-to-grave liability through laws like the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act means companies can be held responsible for the downstream damage their e-waste creates.
Environmental Impact of Improper or Illegal ITAD
Improper disposal of IT assets can lead to environmental contamination. Landfills are not designed to handle e-waste, which contains hazardous components like lead, mercury, fire retardants, persistent organic pollutants, and countless others. When mishandled, these toxins can leach into the environment, causing serious human health hazards. This is why e-waste is now banned in 23 US states, with more soon to follow. If your assets are discovered in a landfill, this not only damages brand reputation but also puts companies at financial risk for cleanup costs and potential lawsuits. This is one of the many reasons why refurbishment and reuse, which promote a circular economy, is always the best option.
Risk of Illegal Export of E-Waste
Despite awareness of the issues, e-waste from developed countries is still often illegally exported to informal, uncertified recycling facilities in developing nations. This practice, driven by the profit from precious metals in e-waste, violates the Basel Convention, which aims to protect developing countries from toxic waste imports. Informal recycling centers pose significant risks as untrained workers, even children, handle hazardous materials without proper safety measures, leading to severe health and environmental impacts. Again, if your retired assets are discovered in one of these centers, it could damage your brand reputation.

Image by Muntaka Chasant, CC BY-SA 4.0, showing informal e-waste recycling in Ghana with the open burning of electrical wires to extract valuable metals.
ICT: An ITAD Managed Service Provider Setting High Standards for ITAD
ICT is an ITAD managed service provider (ITAD MSP) that uses a nationwide team of vetted logistics handlers specializing in the secure transportation of IT assets. They also have close relationships with numerous nationwide processors and know exactly who to send which assets to maximize reuse and, therefore, residual asset value. Their certified processors are skilled in performing stringent NIST 800.88 data destruction procedures, including the verification of erasure of every drive. Non-reusable assets are responsibly recycled in vetted US facilities in strict adherence to environmental regulations.
Throughout the ITAD lifecycle, their clients can track assets online by serial number or location, download certificates of responsible recycling and data destruction, and obtain audit-ready, streamlined records, ensuring compliance and minimizing risk all without them having to lift a finger. At the end of the process, most of their customers receive residual cash value that they can put back into their IT budget. Getting a premium service at no cost, let alone getting paid for that service, is exceptionally rare. Why engage in risks like DIY ITAD when you can have everything handled for you while maximizing your residual asset value?
Case Study 1: ICT performed ITAD services for a New York office of a global media conglomerate to securely dispose of 582 lbs. of various used IT equipment. They ensured that data was erased according to NIST 800.88 protocol and that disposal was compliant with the R2 Responsible Recycling standard. This project minimized the impact on the environment while ensuring maximum data security for their client.
Case Study 2: ICT has been working with a major pharmaceutical manufacturer. To date, cooperation with Mission Reuse has generated $40,000 in positive cash flow that they were able to put back into their IT budget.
The Bottom Line
DIY ITAD may appear cost-effective, but it carries significant risks and hidden consequences. Proper IT asset disposition demands expertise in data security, environmental responsibility, and regulatory compliance. Partnering with a professional ITAD provider ensures these critical areas are managed effectively, safeguarding your company from financial, legal, and reputational harm. Additionally, entrusting ITAD to professionals eliminates inefficiencies, allowing your tech team to focus on their core responsibilities. ITAD experts provide a faster, more efficient, and cost-effective solution for managing IT asset disposition.
Find Out How We Can Help
If you are an enterprise, government, or institution looking for ITAD solutions or have additional questions, please contact us at ICT. Also, take a look at our white paper on ITAD in Today’s Circular Economy, exploring this concept in depth.
Selected References
Basel Convention. (2011). Www.basel.int. https://www.basel.int/TheConvention/Overview/tabid/1271/Default.aspx
Bloomberg. (2023, December 12). Consumer Data Privacy Laws. Bloomberg Law. https://pro.bloomberglaw.com/insights/privacy/consumer-data-privacy-laws/
ERCC. (n.d). Map of States With [E-waste] Legislation. Www.ecycleclearinghouse.org. https://www.ecycleclearinghouse.org/contentpage.aspx?pageid=10#:~:text=There are currently 25 states
ICT About ICT (n.d.) ICT About Company Page. Retrieved February 2, 2024, from https://ictcompany.com/
ICT Mission Reuse (n.d.) ICT Mission Reuse. Retrieved February 2, 2024, https://mission-reuse.com/
Kissel, R., Regenscheid, A., Scholl, M., & Stine, K. (2014, December 17). Guidelines for Media Sanitization. Csrc.nist.gov. https://csrc.nist.gov/pubs/sp/800/88/r1/final
Statista. (2024). Cost of a data breach in the U.S. 2024 | Statista. https://www.statista.com/statistics/273575/us-average-cost-incurred-by-a-data-breach/#:~:text=Published by Ani Petrosyan%2C Sep
US EPA. (2018, August 15). Summary of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act | US EPA. US EPA. https://www.epa.gov/laws-regulations/summary-resource-conservation-and-recovery-act
©ICT Inc. 2024-2027. All rights reserved. Unauthorized reproduction, distribution, or use of this article, in whole or in part, without proper attribution to ICT Inc. is strictly prohibited.
